In the early days, computers were bulky, inaccessible machines, or were accessed through terminals that were essentially an extension of the machine.
Personal computers enabled computing to occur in a much more decentralized way.
Personal computing was the most common computing model for a time. Applications ran and data was stored locally on a user’s device, or in some instances in an on-site data center.
Have you heard about the term Edge Computing?
In a distributed computing framework, computation is placed near the edge where people and things produce or consume data.
What Is Edge Computing?
According to Gartner, edge computing is defined as a part of a distributed computing architecture where information processing takes place near the edge.
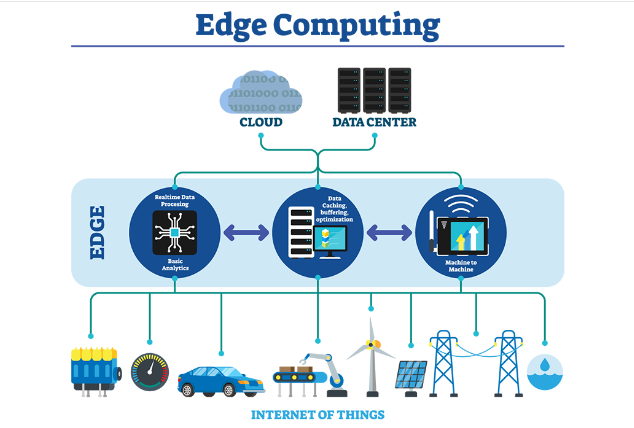
Edge computing is a basic procedure of bringing computation and data storage nearer to the devices where they are gathered, rather than relying on a central location that is thousands of kilometers away. To avoid latency issues that may affect application performance, data, particularly real-time data, is processed near the devices where it is collected.
What Is The Need For Edge Computing?
Edge computing has been developed because of the large number of IoT devices that connect to the internet to either send or receive data. As IoT gadgets generate incredible amounts of data during operation, many IoT devices connect to the internet to send or receive info.
In addition, companies can save money by doing the processing locally, resulting in fewer data needing to be processed in a centralized or cloud-based location.
How Edge Computing Is Different From Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing, a newer technology, offers a number of advantages over locally based, on-site computing. Cloud services are centrally managed by vendors and are accessible from any device over the Internet.

While cloud services are often operated from data centers that are distant from their users, edge computing uses proximity to users to minimize data transit times. In cloud computing, resources are shared among a whole group of users, but in edge computing, resources are shared among a smaller set of users. Computing is moved closer to the user in edge computing to minimize data transit times while retaining the cloud computing model. Applications running on the device itself or on the network edge are controlled by a single entity in edge computing.
What Are The Real-Life Applications of Edge Computing?

Given below are the examples of Edge Computing:
To Monitor The Entire Manufacturing Process
Edge computing can be used in the manufacturing sector in order to monitor the processes and also to apply the machine learning(ML) and analytics in real-time scenarios that will help in product quality improvement. It is also vital in detecting errors in production during the manufacturing process.
Sensor-equipped Educational Toys
In edge computing, data is processed locally rather than being sent to the cloud, which enables school districts to take advantage of IoT devices. Dan Reed, senior vice president for academic affairs at the University of Utah, believes that sensor-equipped educational toys can provide information about behavior and social dynamics. In addition to gathering safety data in playgrounds, you can gather some really interesting information on the low end of computing capacity. For example, cameras can be used to track eye movements in order to better understand how children learn to read.
Enable Performance-enhancing System
Edge computing’s real-time feedback capabilities might fuel performance-enhancing learning systems. According to Daniele Loffreda, we may add machine learning and artificial intelligence that can respond depending on what the student provides into the learning platform – adapt the prompts and learning to fit that student’s way of life, a senior consultant with Ciena, explains. Edge computing can help this happen in real-time.
Usage in Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous cars consist of various types of sensors that create a large amount of data. This sensor data needs to be processed quickly. Thus, Edge computing enables vehicles and other connected devices to process their data in close proximity. This way, it saves cost.
What Are The Issues In Edge Computing That Needs To Be Worked Upon?
Connectivity Issues
Although edge computing bypasses common network restrictions, even the most tolerant edge deployments require some level of connectivity. It’s vital to plan an edge deployment that can handle sporadic or poor connection, as well as what occurs when connectivity is lost. Edge computing requires autonomy, artificial intelligence, and graceful failure planning in the event of connection issues.
Security Issues
Because IoT devices are extremely insecure, it’s critical to plan an edge computing rollout that prioritizes proper device management, such as policy-governed configuration prosecution, as well as protection in computing and storage resources, such as security patches, with a focus on data encryption at rest and in flight. Secure communications are included in IoT services from major cloud providers, but this isn’t always the case when creating an edge site from the beginning.
Lifecycles of Data
The recurrent problem with today’s data avalanche is that so much of it is useless. Consider a medical monitoring device: only the issue data is important, thus maintaining days of normal patient data is pointless. The majority of the data used in real-time analytics is temporary and not maintained for lengthy periods of time. After doing an analysis, a company must pick which data to preserve and which to delete. Furthermore, the data that is kept must be secured in compliance with company and regulatory rules.
Conclusion
It is predicted that in the year 2021 to 2026, the edge computing market size will grow from 36.5 billion to 87.3 billion according to a CAGR of 19% as per the given forecast period. In a nutshell, edge computing assists in decentralizing the data processing and helps to lower cloud dependence.
To keep up with the latest technology the young learners need to start early. They need to enroll in online coding classes for kids to get fundamental knowledge about the innovative technologies of AI, IoT, and Robotics.
 2046
2046

